Relying on our ample network of 3 500 experts and certified trainers…
We implement projects in various fields of development cooperation.

Our trainers and experts do not only offer specific expertise in the required field of activity but also possess valuable knowledge of the region or country we are working in.
We have longstanding experience in:
-

The conduction of field studies, impact assessments and evaluations.
-

The conceptualization and implementation of trainings and workshops
-

The realization of short, middle and long-term projects
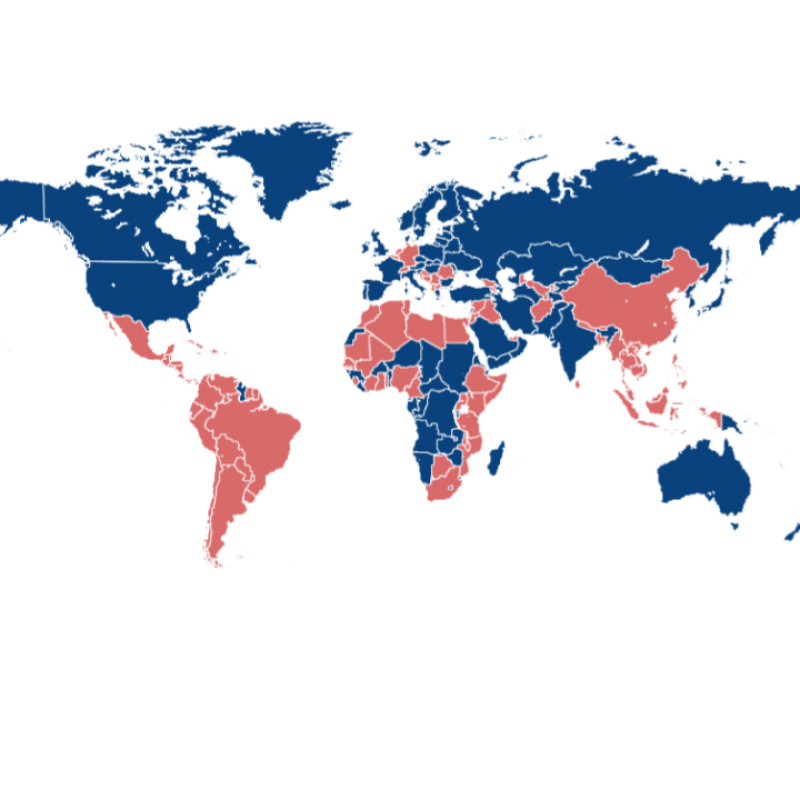
We are a development consulting organisation that differs from the norm!
We put together solutions that draw on competent resources from our global CEFE network, so that we can offer the market a mix of appropriate local, regional and international expertise.
Private Sector Development
CEFE International provides knowledge in implementing different Private Sector Development approaches for the sustainable development of this sector. We use a number of approaches and instruments of evaluation with focus on interventions promoting growth through inclusivity and eradiation of inequality, including the support of Entrepreneurs in improving the performance of their enterprises through Business Development Services (BDS) or connecting informal MSME with the register and formalize market. Furthermore, linking the public and private economy through public-private partnerships, value chain management, specialized measurements for women´s entrepreneurship development and improving business environment.
Enabling Economic Environment
It is well known that economic growth and job creation goes hand in hand with an entrepreneurial environment, because small and medium enterprises are key players in economic development. In a lot of post-colonial countries, the public sector became very dominant and developed an environment that does not support people to start their own business. Examples for missing governmental macroeconomic factors are stability, well-defined property rights and sometimes subsidies, that only support the survival of existing businesses.
To develop an entrepreneurial environment, entrepreneurs need to have access to capital, labour, markets and good management skills. Governments need to get into a dialogue with the private sector to address the right topics (Public private dialogue). In a lot of developing economies, the informal sector also plays a major role and governments need to find ways to include this sector into their economies instead of fighting against them.
Education, vocational qualification and labour market development
Obtaining a quality education is the foundation to improve people’s lives and sustainable development. However, until today, education remains an inaccessible right for millions of humans around the world, especially in conflict-effected areas. Over 72 million children of primary education age are not in school. As the most affected area, in Sub-Sahara Africa, more than half of the children have never been enrolled in school live. Furthermore, around 780 million adults are illiterate and do not have the necessary tool-set to improve both their living conditions and those of their children.
Seen as the single-most important driver of economic empowerment for individuals and countries, the crucial role of education in achieving sustainable development is consequently obvious. Education has shown positive effects in increased economic and community development, benefits in food security, improved social, cognitive and health outcomes and gender equity.
Rural Development
Industrial and service sectors are mostly concentrated in the cities, while in rural areas agriculture plays a predominant role. The standard of living and the level of development in rural regions is often lower than in urban areas. Large disparities in living conditions between cities and rural areas may pose potential conflicts.
Often, there is a lack of jobs in the countryside which leads to rural depopulation. Especially young people try their luck in the cities. In developing countries, however, rural migrants often end up in urban slums, where living conditions are not significantly higher.
80 percent of the hungry live in rural areas (50% small farmers, 22% landless agricultural workers, 8% fishermen, ranchers, etc.). Combating world hunger and poverty must consequently focus on rural areas. Rural development therefore enjoys high priority in development policies worldwide and is a key factor in the ‘Agenda 21’ of the United Nations.
Peace Development
With almost half of the world’s poor expected to live in countries affected by fragility, conflict and violence (FCV) by 2030, addressing this challenge remains a main concern for the achievement of individual and economic growth and thus, a high priority for sustainable development. Peace enforcement involves the application of a range of coercive military or civilian measures.
Peace enforcement is furthermore closely related to the following other activities of intervention: conflict prevention, peacemaking and peacekeeping. They rarely occur in a linear or sequential way. As Peace enforcement cannot solve the underlying problems in most areas of potential application and does not create the conditions for lasting peace, experience has shown that they should be seen as mutually reinforcing. If they are used piecemeal or in isolation, they fail to provide the comprehensive approach required to address the root causes of conflict and hence reduce the risk of conflict recurring.
Sustainable Economy
Climate change, ozone depletion, environmental pollution and an immense loss of biodiversity and natural resources through an enormous economic and population growth worldwide express factors that threaten health and the world.
Sustainable business, refers to enterprises that face those challenges and thus have minimal negative impact on the global or local environment, community, society, or economy and often represent progressive environmental and human rights policies. Through green jobs within these businesses, that are linked to the use of clean energy and instruments and the production of green materials, a contribution to the reduction of greenhouse gasses is guaranteed. Seen as a triple win, green development within a business can thus create value for customers, investors and the environment. For example, the demand of sustainable products appears to be increasing worldwide as the green economy grows.
CEFE International, together with its expert, supports knowledge and long-term experience with Green Business Management and the implementation of extra green measures. One example here is the improvement of production processes and business practices of SMEs.
Along the years we have been supporting MSMEs promotion by:
Private Sector Development.

Enabling Economic Environment.

Education, vocational qualification and labour market development.

Rural Development.

Peace Development.

Sustainable economy.
Privacy Overview
Read Our Cookie Policy
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.
